Why Does Yahoo Keep Opening in Chrome? Easy Fix (2025)
Confused as to why Yahoo keeps opening in Chrome when you launch the browser or open a new tab? It's likely because Yahoo is set as your default homepage or search engine. This setting might be changed without your direct consent while installing or updating programs.
This issue is commonly caused by browser hijacking, where unauthorized changes are made to your browser setup. Malicious extensions or software can modify browser settings without your knowledge. These alterations can redirect your searches, change your homepage, and even track your internet activity.
Browser hijackers not only disrupt your browsing experience but can also pose significant privacy and security risks. You can fix this by tracking your browser extensions and removing any unwanted programs. I’ve created a step-by-step guide that covers all the solutions to help you fix the “why does Yahoo keep opening in Chrome” issue.
Editor's Note: Transparency is one of our core values at vpnMentor, so you should know we are in the same ownership group as ExpressVPN. However, this does not affect our review process.
Why is Google Chrome Using Yahoo Search?
There can be multiple problems that can cause Chrome to use Yahoo search. Here are some that you should know about:
- Security software settings. Programs like McAfee LiveSafe’s WebAdvisor might switch your search engine to Yahoo to enhance safety. This change is intentional under the software's protective features rather than a hijacking.
- Network policies. If you’re on a corporate or public network, administrators might enforce specific search engines to ensure uniformity and security across all devices.
- Browser hijacking. If neither of the above seem to fit your situation, you're most likely dealing with a browser hijacker.
What is a Browser Hijacker?
A browser hijacker is a type of malware or potentially unwanted program (PUP) that modifies a web browser's settings without your permission. This typically results in unwanted changes in the home page, new tab page, and default search engine. The primary motive behind these hijackers is often to increase advertising revenue by redirecting users to specific websites, displaying additional ads, or capturing your data traffic.
Browser hijackers can also track your online activities, collecting data such as search queries and browsing history. This data can be used for marketing purposes or sold to third parties. While some browser hijackers are merely annoying, others can be more intrusive and compromise your privacy.
How Do Browser Hijackers Infect Your Device?
Browser hijackers commonly infect devices through several channels:
- Bundled software installations. They're often hidden in the installation packages of free software available online. You might inadvertently install a hijacker if you skip customizing the installation settings and leave additional bundled software selected.
- Malicious links or ads. Simply clicking on a malicious link or deceptive advertisement can trigger a hijacker's download. This often occurs without any clear notification or consent.
- Fake updates or system alerts. Some hijackers disguise themselves as essential system or software updates. These phony alerts can deceive you into installing malware, thinking you're updating something legitimate.
- Email attachments. Hijackers can also arrive via email attachments. An attachment that looks harmless might contain hidden malware that executes once opened.
- Exploit kits. Found on compromised websites, exploit kits probe for vulnerabilities in your browser and plugins to silently inject hijacker software.
Persistence Techniques of Hijackers
Browser hijackers employ various tactics to maintain their presence on your device, making them challenging to remove. Understanding these techniques can help you better tackle the removal process and secure your device from unwanted re-infections:
- Registry modifications. Hijackers often modify the system registry, which is a database that stores low-level settings for the operating system and installed applications. By adding or changing registry entries, hijackers can ensure they are reactivated every time the computer starts up. This makes them particularly stubborn to get rid of.
- Scheduled tasks. Another sneaky method is the creation of scheduled tasks. Hijackers may set up tasks in your system to automatically reactivate or reinstall themselves at certain times, even after seeming removal. This can occur without any visible signs, quietly running in the background and reinstating the hijacker periodically.
How to Remove the Yahoo Search Engine From Chrome
Experiencing your Chrome browser defaulting to Yahoo unexpectedly is often a sign of a browser hijacker infection. Follow these detailed steps to eliminate the hijacker and restore your preferred settings:
1. Run an Antivirus Scan
If your Chrome browser starts defaulting to Yahoo Search, it's crucial to run a full system scan using an antivirus program. This scan helps detect and remove any malware, including browser hijackers, that might have altered your browser settings. Here’s how to remove browser hijackers on Windows and Mac:
For Windows
Step 1. Open Windows Security (Windows Defender) or your preferred antivirus program.
Step 2. Navigate to Virus & threat protection and click on Scan options.
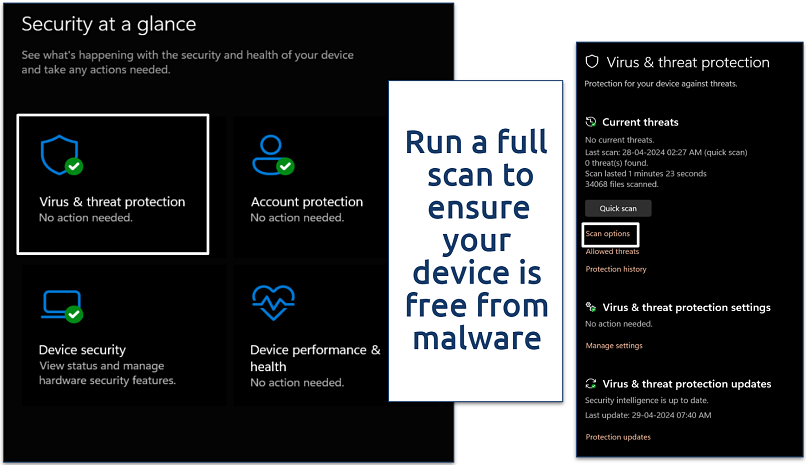 This function also scans your device for other threats
This function also scans your device for other threats
Step 3. Select Full scan and click Scan now to begin a comprehensive scan of your device. This might take some time depending on the amount of data on your system.
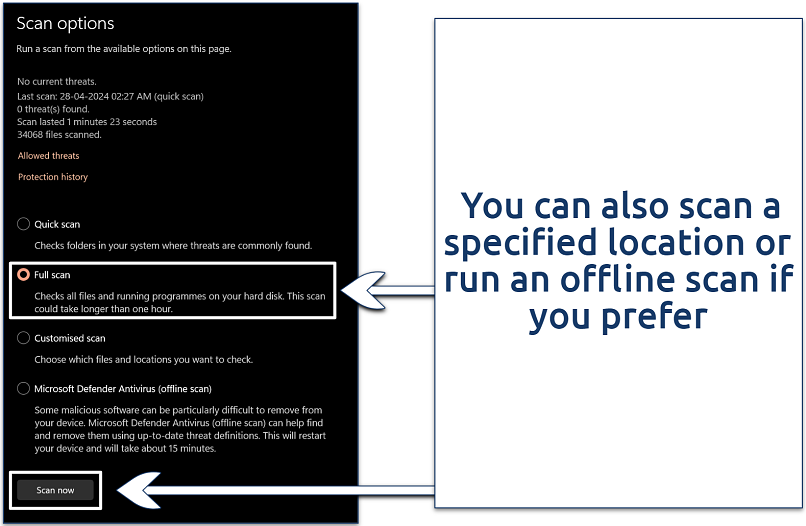 Make sure you have the latest Windows update before running the scan
Make sure you have the latest Windows update before running the scan
Step 4. After the scan, follow the on-screen instructions to remove any detected malware or threats.
For macOS
Step 1. Open Finder, then go to the Applications folder and start your antivirus application. If you haven't installed one yet, consider reputable options like Bitdefender or Norton.
Step 2. Open the antivirus program and select the option for a full system scan.
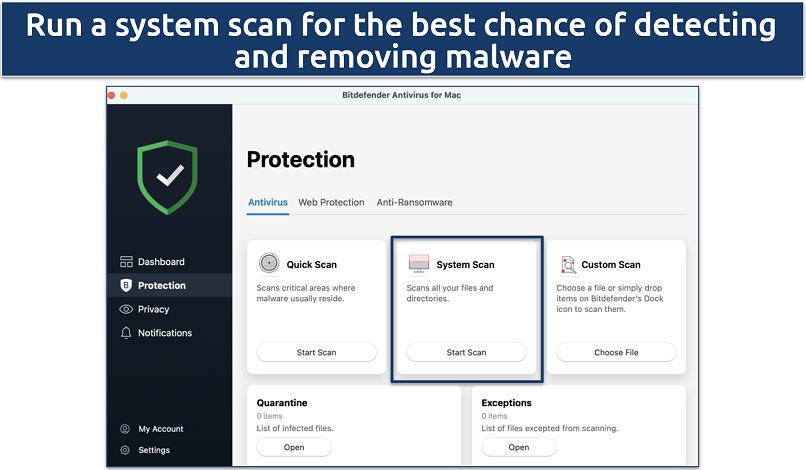 I used the Bitdefender antivirus for Mac
I used the Bitdefender antivirus for Mac
Step 3. Allow the scan to run, which can take a while, depending on the number of files to be checked.
Step 4. Follow any prompts to eliminate found threats, typically involving quarantine or deletion.
2. Change Your Default Search Engine
The purpose of this action is to reset your search engine preference, reversing unauthorized changes.
Step 1. Open Google Chrome. Click on the three dots in the upper-right corner to access the settings menu.
Step 2. Click on Search engine from the sidebar and select Manage search engines and site search.
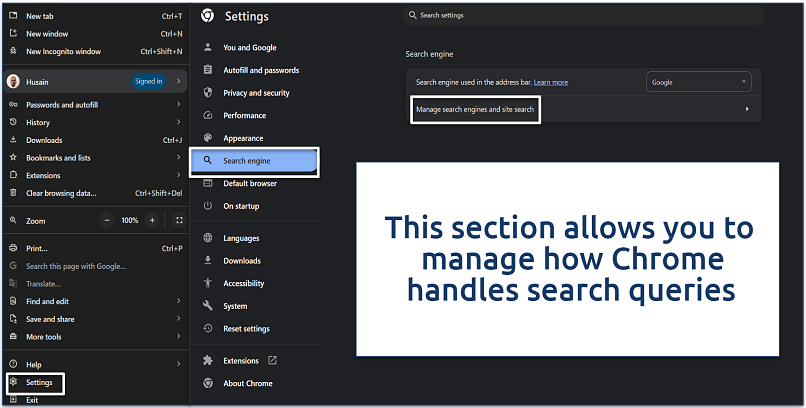 You’ll see a list of all search engines currently configured in your browser
You’ll see a list of all search engines currently configured in your browser
Step 3. To revert your search settings from Yahoo to another search engine like Google, click the three dots next to your preferred search engine and select Make default. This action sets the selected engine as the default for searches performed in the address bar.
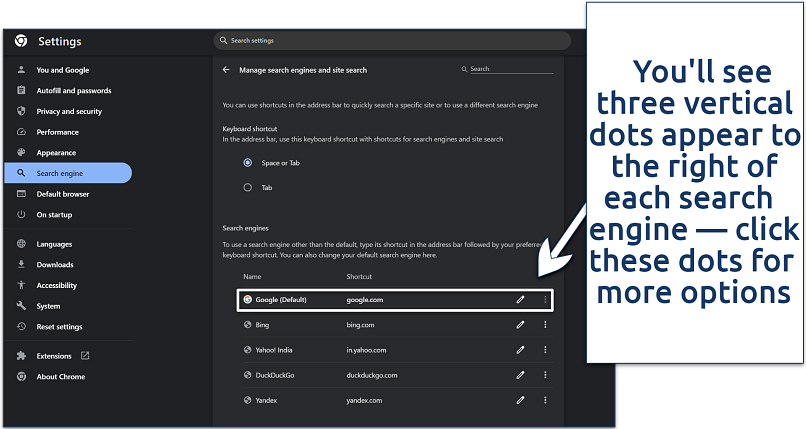 If you notice search engines that you don't recognize, it's best to remove them
If you notice search engines that you don't recognize, it's best to remove them
Step 4. Perform a quick search to ensure the changes have taken effect.
3. Remove Unwanted Extensions
Now, we have to eliminate extensions that could change your settings or monitor your browsing. Regularly reviewing and removing these extensions is crucial for maintaining a secure and efficient browsing environment. Here are the steps to delete unwanted extensions in Chrome on Windows and Mac:
Step 1. Open Google Chrome. Click on the three vertical dots in the upper-right corner to open the menu.
Step 2. Select Extensions and choose Manage Extensions. Carefully review the list of installed extensions. Look for any that you don't recognize or that were not intentionally installed. Click Remove next to any suspicious extensions to delete them.
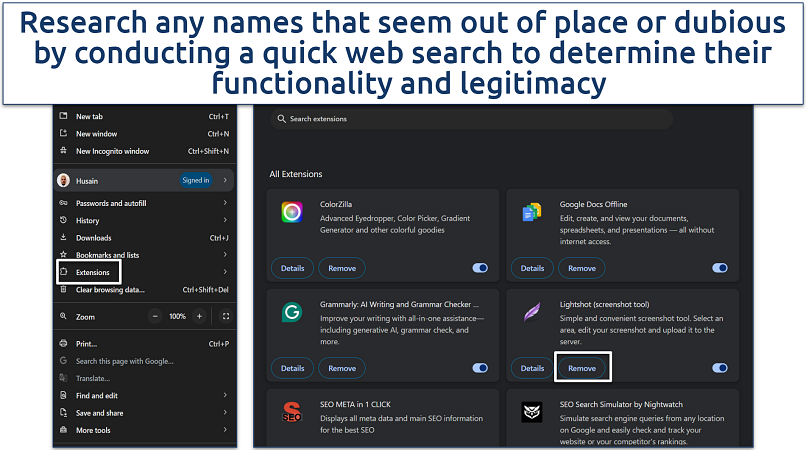 Confirm any prompts to finalize removal
Confirm any prompts to finalize removal
Step 3. Restart Chrome to apply changes and check if the issue persists.
4. Reset Chrome Settings
This process restores the browser to its original state, as it was upon installation, and removes any hijacker-induced changes.
Step 1. Open Google Chrome. Click on the three vertical dots in the upper-right corner to access the settings menu.
Step 2. Click on Settings and select the Reset settings option from the tab on the left. Click on Restore settings to their original defaults. This action will turn off all extensions and clear temporary data like cookies.
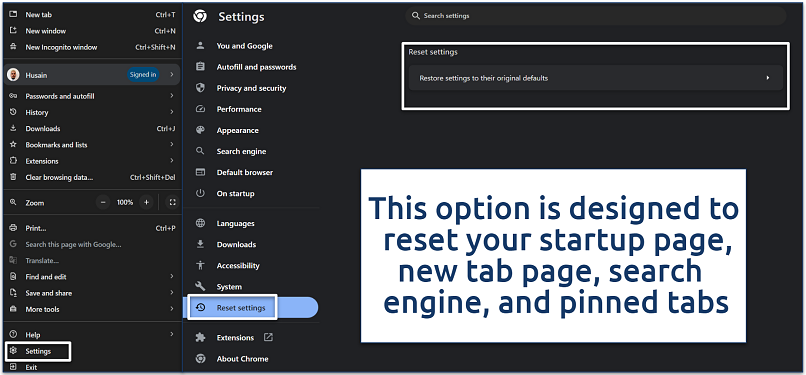 It will also clear cookies and cache, which can remove lingering data from hijackers
It will also clear cookies and cache, which can remove lingering data from hijackers
Step 3. A dialog box will warn you about the reset. Confirm by clicking Reset settings.
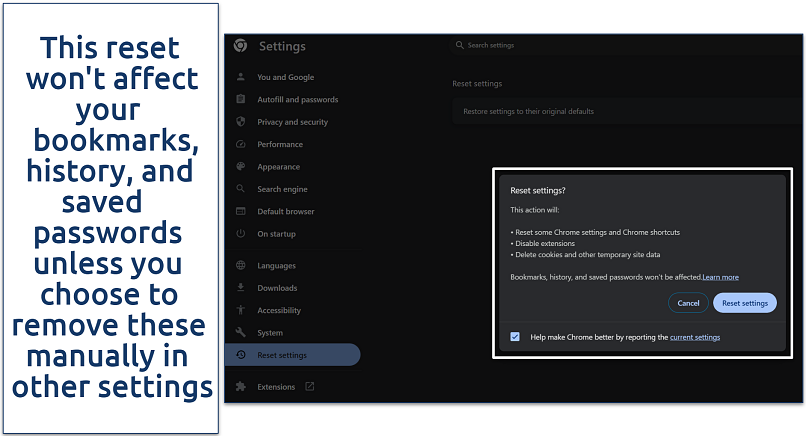 Chrome will restart automatically with the default settings reinstated
Chrome will restart automatically with the default settings reinstated
5. Uninstall Unrecognized Software
Unrecognized or recently added software can often be responsible for changes to your browser settings, including setting Yahoo as the default search engine. Removing these programs is crucial for reversing unwanted modifications and enhancing the overall security of your device.
For Windows
Step 1. Press the Windows key, type Add or remove programs, and press Enter to open it.
Step 2. Scroll through the list of installed applications. Look for any programs installed without your knowledge or that seem suspicious.
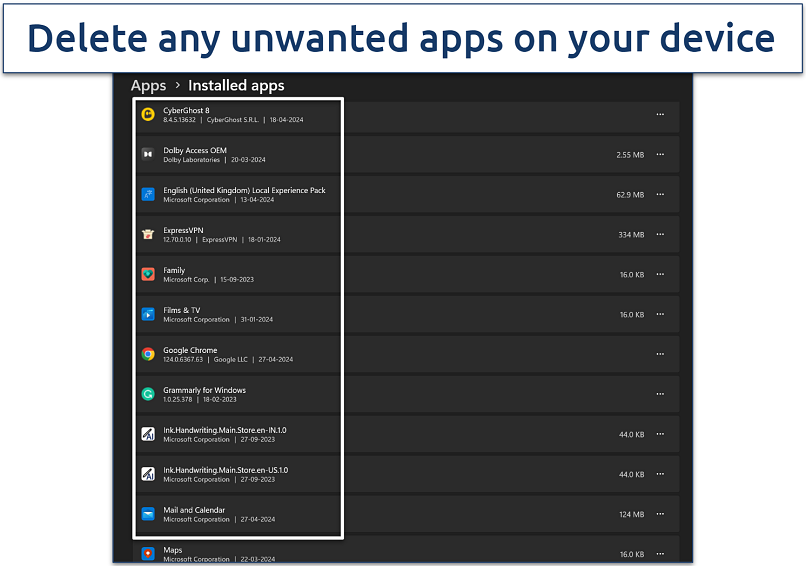 Make sure to backup your data before you make any change
Make sure to backup your data before you make any change
Step 3. Click Uninstall next to any questionable software and follow the on-screen instructions to complete the process.
For Mac
Step 1. Open Finder and click on Applications in the sidebar.
Step 2. Scroll through your applications list to identify any unfamiliar or recently added programs. Drag the suspicious application to the Trash.
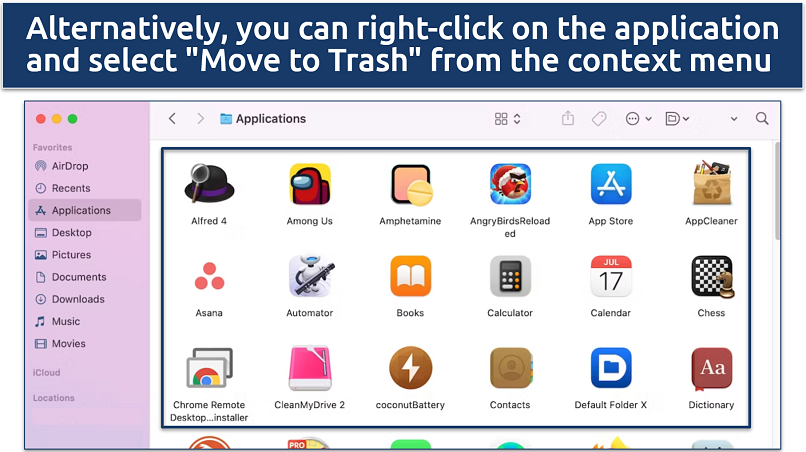 If the app is running, you might be prompted to quit it before it can be moved to the Trash
If the app is running, you might be prompted to quit it before it can be moved to the Trash
Step 3. To permanently remove the applications, right-click the Trash icon in your dock and select Empty Trash.
6. Clear Temporary Files
Temporary files and caches can sometimes harbor malware scripts or settings changes that continuously alter browser behavior. Clearing these files is an important step in removing all components related to hijackers and ensuring optimal browser performance.
Step 1. Open Google Chrome. Click on the three vertical dots in the upper-right corner to access the menu.
Step 2. Select Clear browsing data (or Delete browsing data). Choose the time range All time to ensure all historical data is included. Check the boxes for Browsing history, Cookies and other site data and Cached images and files.
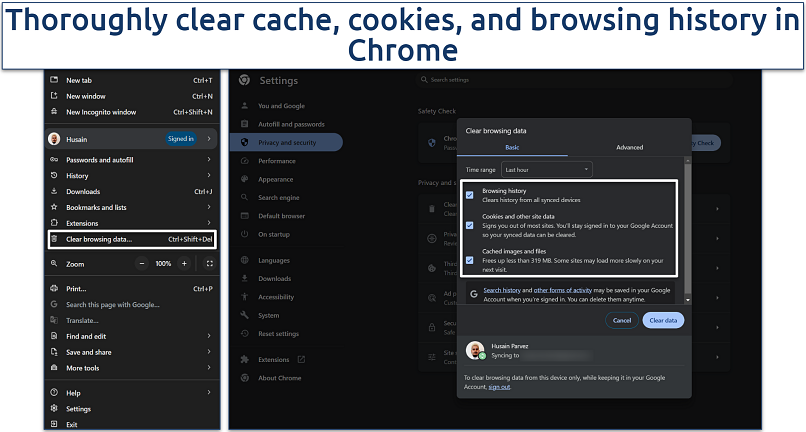 Clear all data to give Chrome a fresh start
Clear all data to give Chrome a fresh start
Step 3. Click on Clear data to finalize the cleaning process. This will help remove any residual files that may be affecting your browser’s settings or performance.
Are Browser Hijackers Only a Problem on Certain Browsers?
Browser hijackers are a universal threat—they aren't limited to any specific web browser. The Yahoo redirect virus operates similarly to its cousins, the Bing and Google redirect viruses. Both the Bing and Yahoo versions manipulate users' browsers to redirect them to different search engines or web pages, aiming to generate ad revenue, often sneaking in through bundled software or dubious browser extensions.
Meanwhile, the Google redirect malware is subtler, covertly rerouting your Google searches to harmful websites without any apparent changes to your browser settings, increasing the risk of phishing and malware.
The ability of hijackers to target any browser underscores the importance of practicing vigilant security measures across all your internet browsing platforms. If you're experiencing issues with your browser and want to reset it to default settings, here are the steps for several popular browsers:
Mozilla Firefox
Step 1. Open Firefox and click the menu button (three horizontal lines) in the upper-right corner.
Step 2. Select Help and then click on More troubleshooting information.
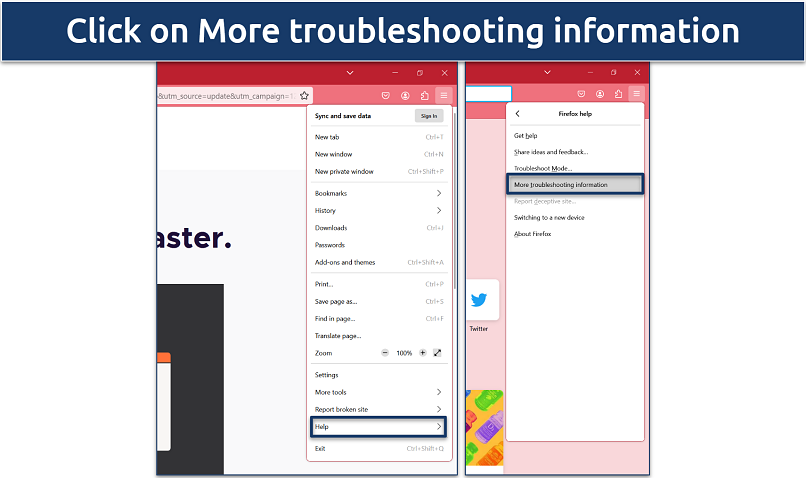 This opens a new tab with information about your Firefox setup, useful for diagnostics
This opens a new tab with information about your Firefox setup, useful for diagnostics
Step 3. Click Refresh Firefox on the right side of the page and confirm it in the pop-up window.
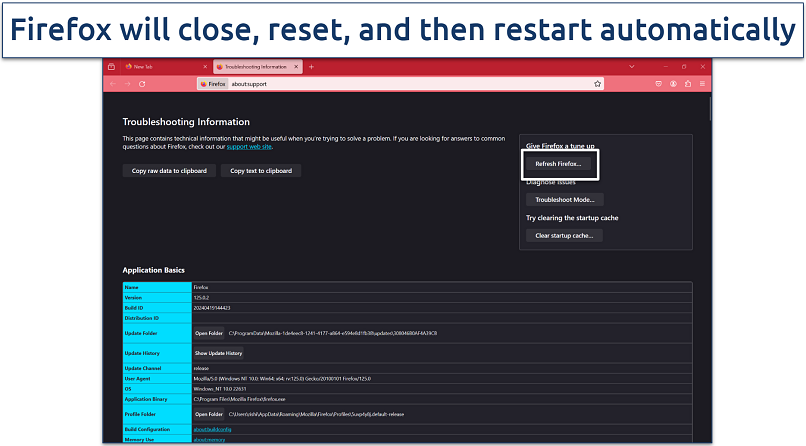 After restarting, Firefox will display a list of the imported information and removed extensions
After restarting, Firefox will display a list of the imported information and removed extensions
Microsoft Edge
Step 1. Open Edge and click the menu button (three horizontal dots) in the upper-right corner.
Step 2. Navigate to Settings > Reset settings.
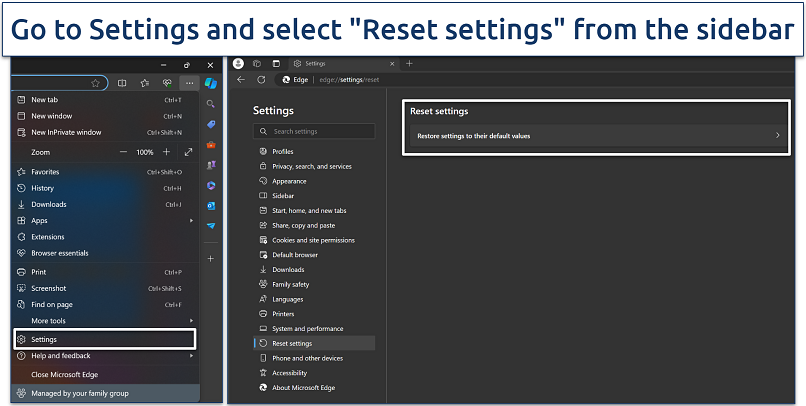 This section provides options to restore settings or clear browsing data
This section provides options to restore settings or clear browsing data
Step 3. Click on Restore settings to their default values and confirm by clicking Reset.
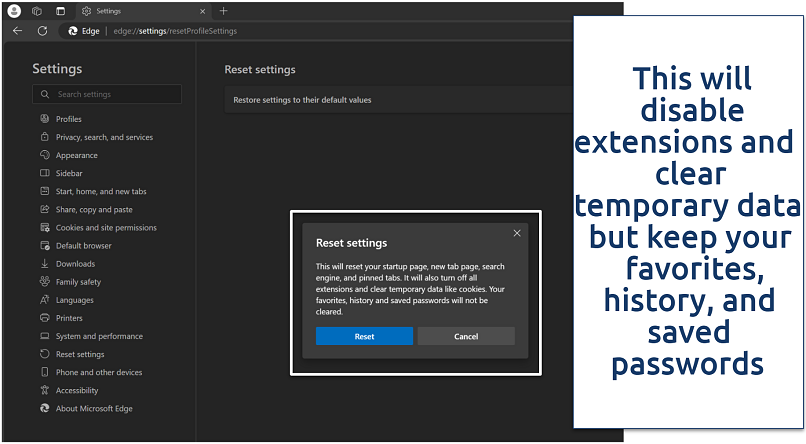 Re-enable any essential extensions carefully, verifying their source and updates
Re-enable any essential extensions carefully, verifying their source and updates
Apple Safari
Step 1. Click on Safari in the menu bar at the top of your screen.
Step 2. Select History and then Clear History. Choose all history from the dropdown menu to remove all browsing data, and click Clear History.
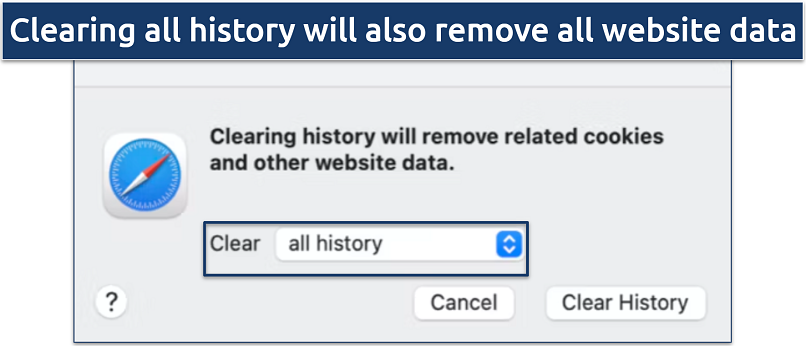 This will also remove all login details and cookies
This will also remove all login details and cookies
Step 3. Next, go to the Advanced tab and select Show Develop menu in menu bar.
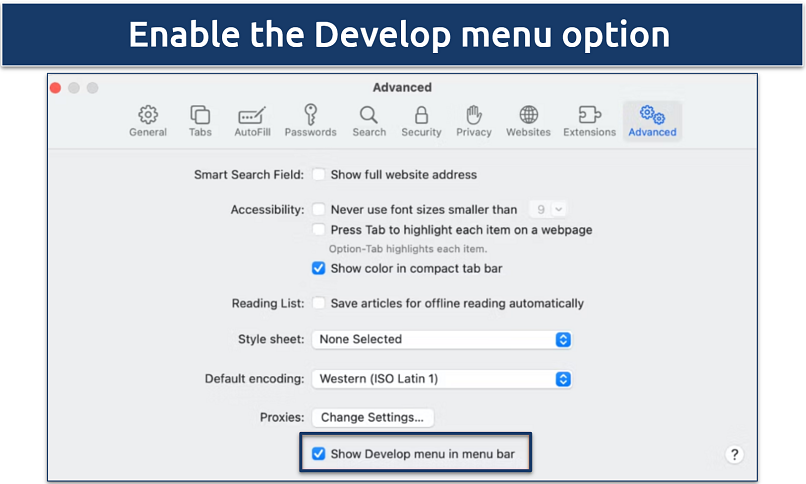 The Develop menu will be visible on the tab above
The Develop menu will be visible on the tab above
Step 4. Click on the Develop menu and select Empty Caches.
Step 5. Choose the Extensions tab and remove any unwanted extensions.
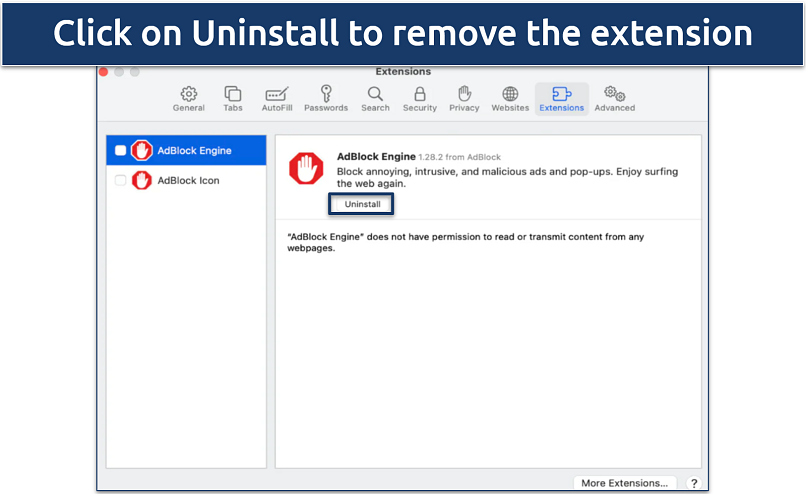 Remove any unwanted or suspicious extensions
Remove any unwanted or suspicious extensions
Pro Tip: If you’re not sure which browser to use, check our expert guides that explore popular browsers and their features in detail:
FAQs on Why Does Yahoo Keep Opening in Chrome
How do I restore my preferred search engine settings in Chrome?
Go to the settings menu and look for the Search engine options panel. Now, go to Manage search engines and site search and set your preferred search engine as default.
How do I prevent Windows from installing unwanted apps?
To prevent Windows from installing unwanted apps, you can adjust your system settings to limit automatic installations. Go to Settings > Apps > Apps & features. Under Choose where to get apps, select the option that restricts installations to the Microsoft Store or the alternative that makes it so administrator approval is needed before apps can be installed. You should also uninstall any unnecessary or suspicious apps already present on your PC.
Can browser hijackers steal my personal information?
Yes, browser hijackers can steal your personal information. While many hijackers primarily aim to redirect your browser traffic for advertising revenue, some are more malicious and are equipped to track your browsing history, capture your keystrokes, and access personal data stored in your browser.
This information can include passwords, account details, and other sensitive data. It's essential to use reputable security software and maintain cautious browsing habits to protect against such risks.
Can I get rid of the malware by uninstalling Google Chrome?
Uninstalling Google Chrome can remove some components of malware, particularly those that are browser-specific or lodged within Chrome’s extensions and settings. However, this does not guarantee the full removal of all malware from your system, as some infections can remain active in other parts of your computer. So, make sure to run an antivirus scan to ensure your system is completely clean.
Wrapping Up: Why Does Yahoo Keep Opening in Chrome?
If Yahoo keeps opening in Chrome, it's likely due to settings altered by browser hijackers, unwanted extensions, or changes made by recently installed software. These adjustments are typically aimed at generating advertising revenue or collecting your data by setting Yahoo as the default search engine without your consent.
To fix this issue, run an antivirus scan, remove any suspicious extensions, reset browser settings, and uninstall any unrecognized software. Regular updates to your antivirus and cautious monitoring of your downloads and installations are also crucial to maintaining a secure browsing environment and preventing unwanted changes.
Your data is exposed to the websites you visit!
Your IP Address:
18.227.46.75
Your Location:
US, Ohio, Columbus
Your Internet Provider:
The information above can be used to track you, target you for ads, and monitor what you do online.
VPNs can help you hide this information from websites so that you are protected at all times. We recommend ExpressVPN — the #1 VPN out of over 350 providers we've tested. It has military-grade encryption and privacy features that will ensure your digital security, plus — it's currently offering 61% off. Editor's Note: ExpressVPN and this site are in the same ownership group.
Leave a comment
Your blog is a treasure trove of knowledge! I'm constantly amazed by the depth of your insights and the clarity of your writing. Keep up the phenomenal work!



Please, comment on how to improve this article. Your feedback matters!