How To Install ExpressVPN on Linux in 2026
- How To Install ExpressVPN on Linux — Easy Guide
- Where Can I Find ExpressVPN’s Linux Commands?
- How To Use ExpressVPN on Linux
- Other ExpressVPN Features and Settings
- How To Install and Use ExpressVPN on Linux Distros Using OpenVPN Client
- How To Setup ExpressVPN on Raspberry Pi
- Advanced Configuration Options
- FAQs
Does ExpressVPN have a Linux app? Yes, and it’s surprisingly easy to set up; we’ll show you all the different methods. Our step-by-step guides explain how to install ExpressVPN for Linux on Ubuntu, Arch, Linux Mint, and other distros.
As Linux only has about a 4% market share¹, many VPNs don’t bother fully supporting it with native apps. Thankfully, ExpressVPN provides a Linux app that’s just as good as its offerings for Windows and Mac. You don’t miss out on any essential features, and it allows you to use a GUI if you’re tired of entering commands.
How To Install ExpressVPN on Linux — Easy Guide
Do Linux devices get viruses? Much less than other operating systems, but your data’s still at risk. An older survey revealed over 90% of Linux users had never had a virus on their device (Government Technology, 2010)2. However, as time has gone on, more sophisticated hackers have developed advanced malware like WolfsBane and FireWood to go after the data on Linux devices (The Record, 2024)3.
Follow the steps below to install ExpressVPN for Linux distros within minutes:
1. Choose Your Installation Method
There are several different ways to install ExpressVPN. While all require using at least some command-line code, they vary greatly in number and technical complexity. Use this brief guide to help you choose the best one for you:
- Command Line Interface (CLI). Heavily terminal-based but still straightforward for advanced Linux users. One of the more complex methods, but it offers full control of the VPN’s behavior and quick actions via CLI commands.
- Browser extension. Requires minimal command-line use to install the browser extension and activate ExpressVPN. You can then use the extension’s graphical user interface (GUI) just like a normal visual app. This is only one of several reasons why it ranks highly amongst our favorite VPN browser extensions.
- OpenVPN configuration. The most complex and customizable. Requires manually downloading configuration files and using advanced terminal commands for setup and management.
- Network manager integration. Requires a few terminal commands initially to install and configure ExpressVPN. Thereafter, you use a combination of GUI elements and command-line arguments to manage VPN connections.
2. Download the Installer
Visit the ExpressVPN website. Navigate to the download section, select Linux as your platform, and choose the package for your specific distribution (e.g., .deb for Debian/Ubuntu or .rpm for Fedora/CentOS).
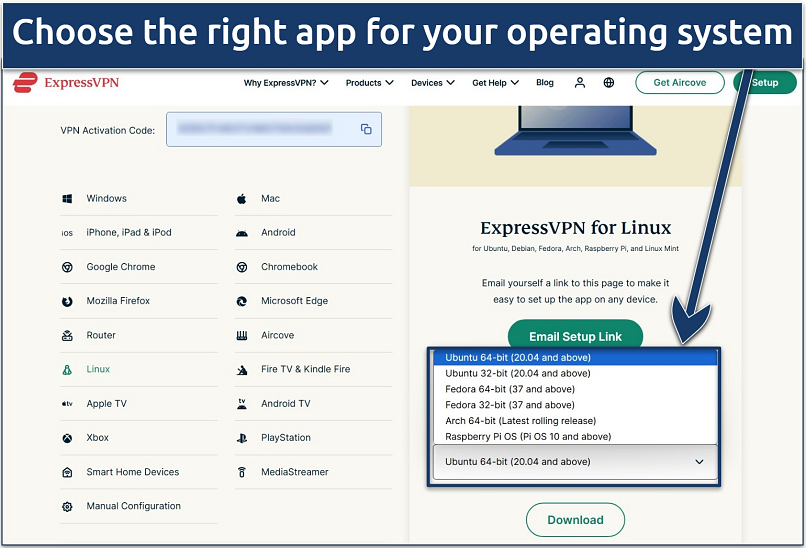 You can easily copy and paste the activation code for later use
You can easily copy and paste the activation code for later use
You can download ExpressVPN for several distros. ExpressVPN has the following installer options to choose from:
- Ubuntu (32-bit and 64-bit)
- Fedora (32-bit and 64-bit)
- Arch (latest rolling release 64-bit)
- Raspberry Pi OS
3. Install ExpressVPN Using the GUI and Command Line
Now that you’ve downloaded the installer on your device, there are only a few more steps required to install ExpressVPN. You can either navigate to your downloads folder using the GUI or run the terminal and enter this command:
How To Install ExpressVPN on Linux Distros Using GUI
You can install ExpressVPN using the GUI (Graphical User Interface). Just right-click the downloaded installer. Choose Open with Other Application > Software Install > Select. The next steps include clicking the Install button, entering your Linux system password, and choosing Authenticate. Once your password is authenticated, it will start the installation.
 After this, simply follow the prompts to authenticate the installation
After this, simply follow the prompts to authenticate the installation
When the installation is complete, go to the terminal and run this command:
How To Install ExpressVPN on Linux Distros Using the Command Line
Depending on the distribution you’re using, run one of the following commands. Keep in mind that the installer filename may be different depending on what version of the app you downloaded.
Ubuntu / Debian / Mint
Enter the following command:
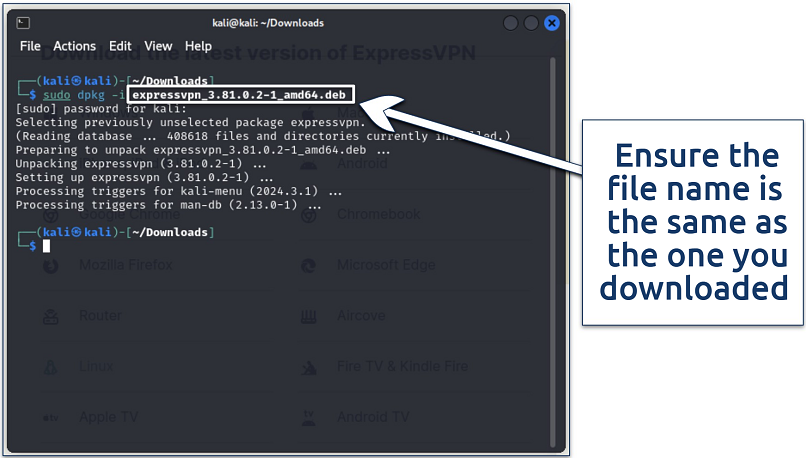 The installation process should only take a few minutes at most
The installation process should only take a few minutes at most
Fedora / CentOS
Enter the following command:
Arch
Enter the following command:
Note. You have to type your user password to install the file. To install ExpressVPN on Arch Linux, enter “y” to proceed with the installation. Use Expressvpn Arch Linux by following the method below.
4. Activate the App
Finally, you can activate the ExpressVPN app on your Linux distro. Just open a new terminal and run the following command:
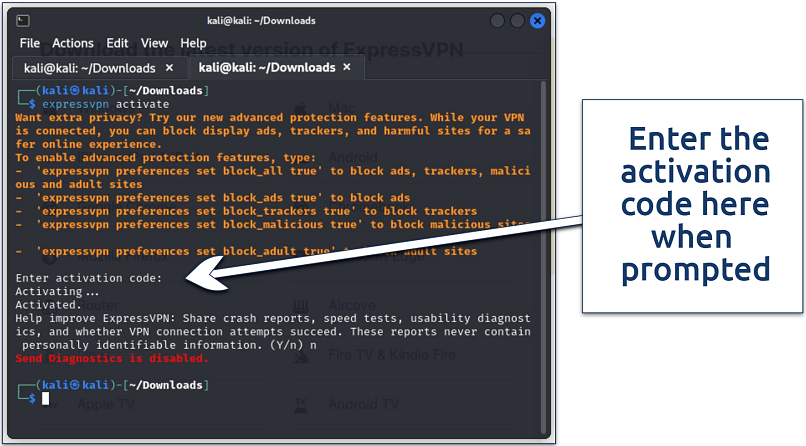 You can choose if you want to share diagnostics at this point
You can choose if you want to share diagnostics at this point
All you need to do now is enter your activation key and select “Y/n” for sharing anonymized diagnostic reports. Enter “Y” to accept or “n” to decline. If you choose yes, but want to opt out, enter the command:
5. Install the ExpressVPN Browser Extension on Linux Distros
You can set up a connection through ExpressVPN’s browser extension. However, it’s not a standalone option; you must use it with the ExpressVPN app first, following the instructions above. The VPN supports Chrome and Firefox, and using the browser extension gives you easy access to the servers through a GUI.
Once you have set up ExpressVPN and want to install the browser extension, just run the following commands:
For Firefox
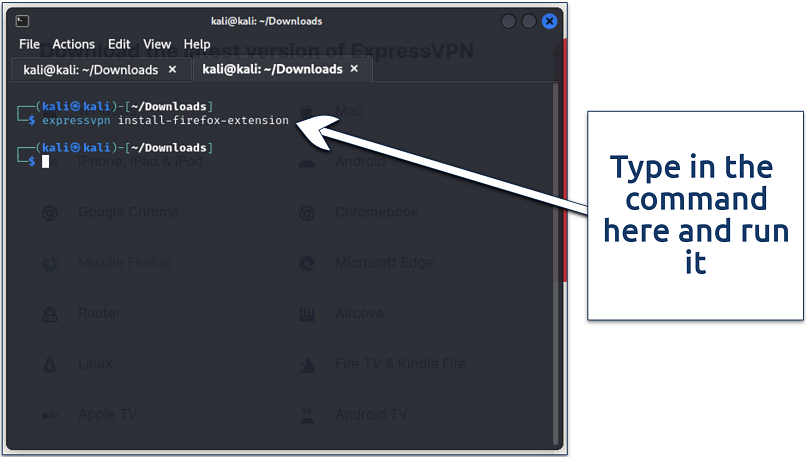 You can only do this once you've installed the base ExpressVPN app
You can only do this once you've installed the base ExpressVPN app
For Chrome
Running the command will launch the appropriate browser with the ExpressVPN extension page:
 You can also go straight to the Chrome Web Store or Firefox Add-ons instead of using the CLI
You can also go straight to the Chrome Web Store or Firefox Add-ons instead of using the CLI
Finally, just follow the prompts to complete the installation for either Chrome or Firefox:
 You can also allow the extension to run in Private Windows/Incognito mode
You can also allow the extension to run in Private Windows/Incognito mode
Where Can I Find ExpressVPN’s Linux Commands?
We’ve compiled a list of the essential commands right here for your convenience. Unless you use the Browser extension, you’ll primarily interact with ExpressVPN via CLI instructions. Although it may seem complex, it’s relatively straightforward once you know some of the most important commands.
For your quick reference, here are a list of useful commands for managing ExpressVPN on Linux:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| expressvpn connect | Connects to the last connected server or the best available location. |
| expressvpn connect [location] | Connects to a specific server location (e.g., expressvpn connect us). |
| expressvpn disconnect | Disconnects from the VPN. |
| expressvpn status | Displays the current VPN connection status. |
| expressvpn list | Lists all available server locations. |
| expressvpn preferences set auto-connect true | Enables auto-connect on system startup. |
| expressvpn preferences set auto-connect false | Disables auto-connect on system startup. |
| expressvpn preferences set protocol [protocol] | Sets the VPN protocol (e.g., lightway, udp, tcp). |
| expressvpn speed-test | Runs a speed test to find the fastest server. |
| expressvpn activate | Activate the app using your activation code. |
How To Use ExpressVPN on Linux
Below is a step-by-step guide to using ExpressVPN on Linux.
Connect to an ExpressVPN Server
Go to the terminal and run this command:
ExpressVPN uses the Smart Location feature to select the nearest server location when connecting for the first time. However, if you’ve used the service before, the VPN connects to the server location you used most recently.
To explicitly use the smart location feature after your first time, use this command:
Once you are successfully connected, you can see the “Connected to…” message written in green. You may also see a notification card on your screen stating that the VPN is connected.
If you use the browser extension, the entire interface will turn green when you’re connected to a server:
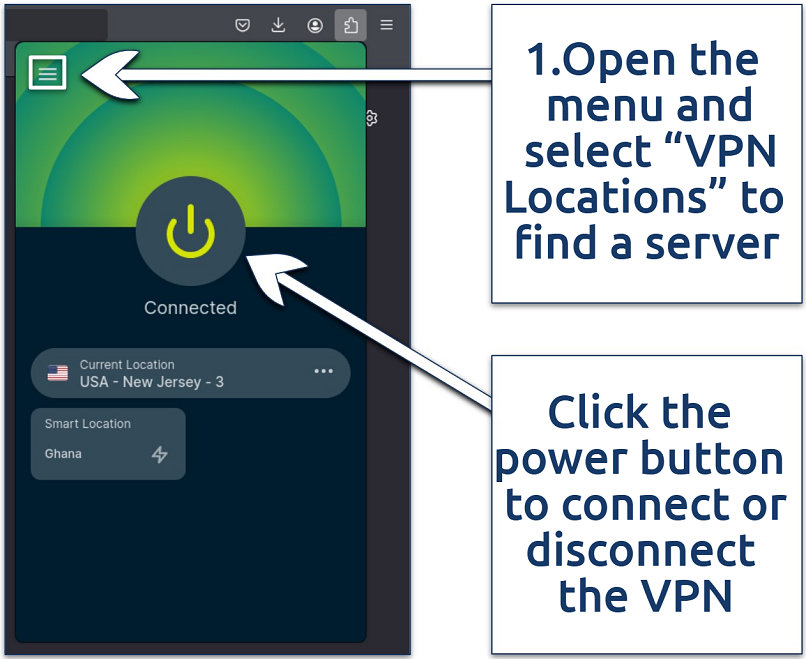 You can also click on the "Smart Location" box to use the feature
You can also click on the "Smart Location" box to use the feature
Disconnect From a VPN Server Location
To disconnect from a server location, run the following command:
ExpressVPN will disconnect from the server it’s connected to. You may also see a notification card stating that the VPN is disconnected.
Choose an Alternative Server location
To find the recommended locations to connect to, enter the following command:
To see all available locations, enter the command:
To connect to a specific server location, type the command:
or
For example, to connect to the London server, enter the command:
or
Be advised. The VPNs we recommend follow strict no-logging policies. This stops them from viewing or recording what you do online. Therefore, you’re fully responsible for how they’re utilized. My team and I urge you to uphold all copyright agreements.
Other ExpressVPN Features and Settings
Switch to a Different VPN protocol
VPN protocols determine how data is routed between your device and a VPN server. By default, ExpressVPN is set to use the automatic protocol option, which should be its proprietary Lightway protocol in most cases. However, switching to a different protocol can give you faster connection speeds.
Note. Ensure you have disconnected the VPN before switching to another protocol.
To Switch to Lightway – TCP
Run this command:
To Switch to Lightway – UDP
Run this command:
ExpressVPN’s proprietary Lightway protocol offers super-fast speeds without compromising on security.
To Switch to OpenVPN – TCP
Run this command:
To Switch to OpenVPN – UDP
Run this command:
To Use the Automatic Option
Once activated, this mode will automatically select the best protocol, depending on your network conditions.
Run this command:
Block Trackers and Malicious Sites
ExpressVPN Linux app also has a Threat Manager feature that protects you against pesky apps, trackers, and malware. Threat Manager blocks all communications with servers listed as trackers or malicious sites.
To Enable or Disable Threat Manager
Open the terminal window and enter the appropriate command.
To enable Threat Manager, enter the following command:
To disable Threat Manager, enter the following command:
Note. Make sure to connect to the VPN network and use the automatic protocol or Lightway.
Open the App Manual
To see the full list of the app’s functions, run the following command:
After typing any command, you can also hit the tab key twice to see all the available options. For example, typing: “expressvpn protocol” and hitting the tab key twice shows all available protocols.
Use the Auto-Connect Feature
ExpressVPN has a feature that allows it to automatically connect to the last location you used upon OS startup. This is particularly handy if you frequently use the same server.
It can be done by entering:
Note. You will see the “Auto-connect is enabled” message.
To disable this feature, run the command:
Update the App
Updating the ExpressVPN app on Linux is easy. When an update is available for download, you’ll see the message “a new version is available” in the terminal. Follow the link attached in the notification to update the app.
You can also manually check if your app is using the latest version. Here’s how to update ExpressVPN on Linux:
Step 1: Check the latest Linux app version.
Step 2: Run the following command:
Step 3: Use the ExpressVPN for Linux download page to get the latest installer file compatible with your distro.
Step 4: Install the newest version of the app.
Uninstall the App
Finally, if you don’t want to keep on using ExpressVPN, follow the process below to uninstall the app:
Ubuntu / Debian / Mint
Type the command:
Fedora
Type the command:
Arch
Type the command:
How To Install and Use ExpressVPN on Linux Distros Using OpenVPN Client
It’s possible to set up ExpressVPN on Linux using the OpenVPN protocol. To do this, go back to the Download page of your ExpressVPN account and click on the Manual Configuration option. You should see your username, password, and a list of OpenVPN (“.ovpn”) configuration files for servers in different countries. Download the file for the specific server(s) you want to connect to.
OpenVPN is one of the most widely used open-source protocols, known for its security and speed. It’s one of the best options to keep you safe across a variety of online tasks, from streaming to banking, which is why we recommend using it.
Depending on your Linux distribution, enter the commands below:
Ubuntu / Mint
- Enter the following command in the terminal window:
$ sudo apt install openvpn openvpn-systemd-resolved - Then, enter your password and type in “Y” when prompted.
- Next, run the following command to launch OpenVPN. Replace [path to file] with the path to where you downloaded the ExpressVPN configuration file, and [server location] with the location name in the .ovpn file.
$ sudo openvpn --config /[path to file]/my_expressvpn_[server location].ovpn --script-security 2 --up /etc/openvpn/update-systemd-resolved --down /etc/openvpn/update-systemd-resolved --dhcp-option 'DOMAIN-ROUTE.' --down-pre - Finally, enter the username and password you got from ExpressVPN earlier. A message with “Initialization Sequence Completed” will show if the connection is successful.
Debian
- Enter the following command in the terminal window:
$ sudo apt install openvpn resolvconf - Again, enter your password and “Y” at their respective prompts.
- Locate the .ovpn file you downloaded earlier. Type the following command in the console and replace [path to file] with the file path and [server location] with the one in the file. Run the command to try and establish an OpenVPN connection.
$ sudo openvpn --config /[path to file]/my_expressvpn_[server location].ovpn --script-security 2 --up /etc/openvpn/update-resolv-conf --down /etc/openvpn/update-resolv-conf - You’ll then be prompted to enter the username and password from the manual configuration setup page. Wait for the success message.
For Fedora / CentOS
- Enter the following command in the terminal window:
$ sudo dnf install openvpn - Then, execute the following commands in sequence to set up your DNS:
$ sudo cp /usr/share/doc/openvpn/contrib/pull-resolv-conf/client.{up,down} /etc/openvpn/$ sudo chmod +x /etc/openvpn/client.{up,down}$ sudo sed -i -e 's|bresolvconfb|ignore-&|' /etc/openvpn/client.{up,down} - And, then run this command to launch OpenPVN. Replace [path to file] and [server location] with the particulars of the .ovpn file you downloaded earlier:
$ sudo openvpn --config /[path to file]/my_expressvpn_[server location].ovpn --script-security 2 --up /etc/openvpn/client.up --down /etc/openvpn/client.down
Note: It’s best not to close this terminal window to keep the VPN connection active. You can minimize it if you want.
How To Setup ExpressVPN on Raspberry Pi
Raspberry Pi OS, based on Debian, runs on ARM architecture, which is not supported by the official ExpressVPN app. However, you can use OpenVPN with ExpressVPN’s configuration files, a lightweight and reliable option for ARM-based devices. So, simply refer to our OpenVPN Guide for Linux, and follow the Debian instructions, to install it on your Raspberry.
However, it’s very important that you ensure your Raspberry Pi is updated to the latest version to ensure that everything goes smoothly. You can do that using the following CLI command:
Advanced Configuration Options
These advanced configuration options are for Linux power users. They allow you to seamlessly manage VPN connections, startup automation, and integration with your system. Two popular methods include integrating OpenVPN with Network Manager for GUI-based control and setting up a systemd service for automatic connection on boot:
Network Manager Integration
Integrating OpenVPN with Network Manager provides a graphical way to manage your VPN connections.
Follow these steps to set it up:
- Install Network Manager plugins. Open the terminal and run the following command to install Network Manager and OpenVPN:
sudo apt install network-manager-openvpn-gnome - Open Network Settings. Go to your system's Network Manager and select VPN Settings.
- Import configuration. Click Add, choose Import from file, and select your .ovpn configuration file.
- Enter VPN credentials. Input your username and password from the ExpressVPN manual configuration page.
- Connect to VPN. Save the settings and enable the VPN from Network Manager's menu for quick server switching.
Systemd Service Setup
systemd automates the VPN connection on system startup and ensures that it reconnects automatically if it disconnects. All popular distros have systemd by default (Debian, Red Hat-based, and Arch-based). However, you’ll need to use plenty of CLI instructions to get it up and running.
Here’s how to set it up:
- Copy configuration file. Place your .ovpn file in /etc/openvpn/ directory and rename it for clarity:
sudo cp /path/to/config.ovpn /etc/openvpn/your-config.ovpn - Enable OpenVPN service:
sudo systemctl enable openvpn@your-config - Start the service:
sudo systemctl start openvpn@your-config - Verify the connection:
sudo systemctl status openvpn@your-config - Reconnect automatically. systemd will now automatically restart the service if the connection drops.
FAQs
Is using ExpressVPN with Linux safe?
Yes, using ExpressVPN with Linux is safe. You can install ExpressVPN Linux apps easily by following the guide. The VPN comes with military-grade encryption, a Network Lock (kill switch), and split tunneling to safeguard your data. Plus, Perfect Forward Secrecy constantly changes your encryption key, so no one can intercept your private information.
Does ExpressVPN work with all Linux distros?
ExpressVPN is compatible with most Linux distros. It is officially compatible with multiple Linux distributions, including:
- Ubuntu: 20.04 and above
- Debian: 10 and above
- Fedora: 37 and above
- Arch: Latest rolling release
- Raspberry Pi (armhf): Pi OS 10 and above
- Mint: Linux Mint 20 and above
Does Ubuntu have a built-in VPN?
No, Ubuntu doesn’t have a built-in VPN. However, it offers a Network Manager — an excellent GUI to configure your network settings. It helps manage your VPN connections. You can also use ExpressVPN on Ubuntu by connecting to a server using the terminal.
What should I do if I am experiencing issues with my app?
There are several troubleshooting steps to follow if you’re experiencing problems with the ExpressVPN app. You can check out the terminal commands available with the ExpressVPN app on Linux that can help fix the issues. Try the following steps:
- Update your OS. Most VPNs only support the latest few releases for a variety of Linux distributions.
- Download the latest version of the ExpressVPN app for Linux.
- Connect to a different server location.
- Try changing your VPN protocol.
- Reboot your device and relaunch the app.
Can I use a free VPN instead of ExpressVPN on Linux?
You can, but you’d be putting your online privacy at risk. Free VPNs lack advanced security features. Some have even been caught selling user data and embedding malware into their apps. It’s safer to use ExpressVPN with its robust security features and a money-back guarantee. Plus, it’s compatible with many Linux distros.
The majority of free VPNs are not compatible with Linux. If you do manage to find one that functions on Linux, it's likely to impose restrictions on your connection speeds and available server locations. Additionally, these free services often inundate you with intrusive advertisements, pushing you to opt for their paid subscriptions. If ExpressVPN isn’t for you, there are several other great VPNs for Linux with free trials.
References
- https://www.statista.com/statistics/218089/global-market-share-of-windows-7/
- https://www.govtech.com/security/more-than-90-percent-of-linux.html#:~:text=Of%20the%2022%20percent%20that%20have%20been,in%20internet%20service%2C%20and%20Web%20server%20flaws/
- https://therecord.media/china-hackers-linux-malware-target/



Please, comment on how to improve this article. Your feedback matters!